The Ultimate Guide to Truck Parts Names: A Comprehensive Breakdown for Owners and Mechanics
Introduction:
Truck Parts Names
Trucks are the backbone of countless industries, from logistics and transportation to construction and agriculture. Understanding the various truck parts names is crucial for truck owners, mechanics, and anyone involved in the trucking industry. Knowing the correct terminology allows for effective communication, accurate ordering of parts, and efficient repairs. This comprehensive guide will delve into the major truck parts names, providing detailed explanations and insights to help you navigate the world of truck maintenance and repair. We'll cover everything from the engine and drivetrain to the chassis, body, and electrical systems.
Why Knowing Truck Parts Names Matters:
Why is it so important to know your truck parts names? It's more than just sounding knowledgeable; it's about efficiency, cost savings, and safety.
- Effective Communication: When describing a problem to a mechanic or ordering a replacement part, using the correct terminology ensures clear communication and avoids misunderstandings.
- Accurate Parts Ordering: Ordering the wrong part due to incorrect terminology can lead to delays, frustration, and additional costs.
- Efficient Repairs: Understanding the function of each part allows for quicker diagnosis and more efficient repairs, minimizing downtime.
- Cost Savings: Being able to identify potential problems early on can prevent minor issues from escalating into major, more expensive repairs.
- Safety: Knowing the names and functions of critical components can help you identify potential safety hazards and ensure your truck is operating safely.
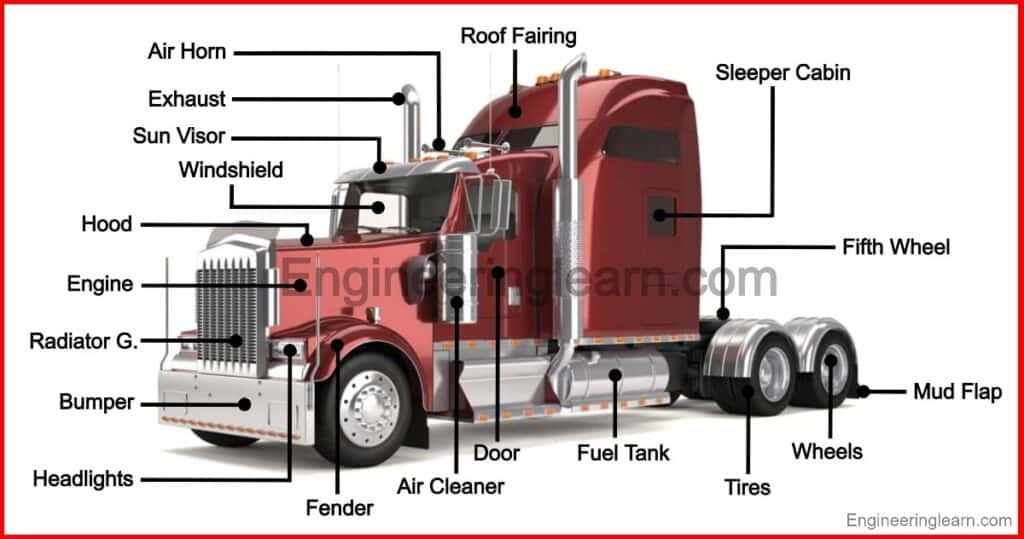
The Engine and Related Components:
The engine is the heart of any truck, responsible for generating the power that propels the vehicle. Here are some of the key engine components:
- Engine Block: The foundation of the engine, housing the cylinders, pistons, and other critical components. It's typically made of cast iron or aluminum.
- Cylinder Head: Sits atop the engine block and contains the valves, spark plugs (in gasoline engines), and combustion chambers.
- Pistons: Move up and down inside the cylinders, compressing the air-fuel mixture and transmitting power to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: Converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion, which is then transmitted to the transmission.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of the valves, regulating the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and exhaust gases out.
- Valves: Intake valves allow air and fuel to enter the cylinders, while exhaust valves allow exhaust gases to escape.
- Turbocharger/Supercharger: Forced induction systems that increase engine power by forcing more air into the cylinders.
- Fuel Injectors: Spray fuel into the cylinders at precise intervals, ensuring optimal combustion.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant through the engine to prevent overheating.
- Radiator: Dissipates heat from the coolant, keeping the engine at a safe operating temperature.
- Oil Pump: Circulates oil through the engine to lubricate moving parts and prevent wear.
- Oil Filter: Removes contaminants from the engine oil, keeping it clean and effective.
- Air Filter: Cleans the air entering the engine, preventing dirt and debris from damaging internal components.

Pro Tip: Regular maintenance, including oil changes, filter replacements, and coolant flushes, is crucial for extending the life of your engine and preventing costly repairs.
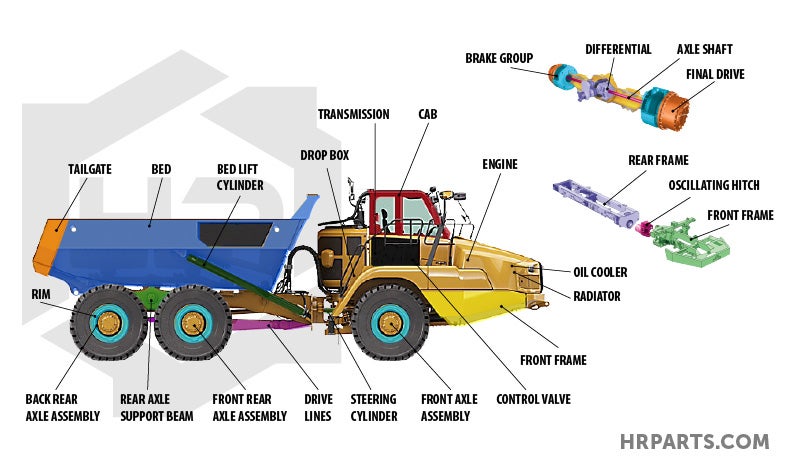
The Drivetrain: Transferring Power to the Wheels
The drivetrain is responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels. Here are the key components:
- Clutch (Manual Transmissions): Connects and disconnects the engine from the transmission, allowing the driver to shift gears.
- Transmission: A gearbox that provides different gear ratios, allowing the engine to operate efficiently at various speeds and loads.
- Driveshaft: Connects the transmission to the differential, transmitting rotational power.
- Differential: Allows the wheels on each axle to rotate at different speeds, which is essential when turning.
- Axles: The shafts that connect the differential to the wheels, transmitting power and supporting the weight of the vehicle.
- Universal Joints (U-Joints): Allow the driveshaft to flex and move as the suspension travels.
Common Mistakes to Avoid: Neglecting drivetrain maintenance, such as lubricating U-joints and checking differential fluid levels, can lead to premature wear and failure.
The Chassis: The Foundation of the Truck
The chassis is the structural framework of the truck, providing support for all other components. Key chassis parts include:
- Frame Rails: The main longitudinal beams that form the backbone of the chassis.
- Crossmembers: Connect the frame rails, providing lateral support and rigidity.
- Suspension System: Consists of springs, shock absorbers, and other components that cushion the ride and maintain tire contact with the road. Common types include leaf spring, air suspension, and independent suspension.
- Steering System: Allows the driver to control the direction of the truck. Key components include the steering wheel, steering column, steering gear, and tie rods.
- Braking System: Responsible for slowing down and stopping the truck. Common types include hydraulic brakes and air brakes.
- Wheels and Tires: Provide traction and support the weight of the vehicle.
Based on my experience: Regularly inspect your tires for wear and tear, and maintain proper tire pressure to ensure optimal performance and safety.
The Body: Protecting the Cargo and Occupants
The truck body provides protection for the cargo and occupants. Key body parts include:
- Cab: The enclosed compartment where the driver and passengers sit.
- Hood: Covers the engine compartment.
- Fenders: Protect the wheels and prevent debris from being thrown onto the body.
- Doors: Provide access to the cab.
- Cargo Box/Bed: The area where cargo is carried.
- Tailgate: The hinged door at the rear of the cargo box.
- Bumpers: Protect the front and rear of the truck from damage in collisions.
- Mirrors: Provide visibility to the rear and sides of the truck.
The Electrical System: Powering the Truck's Functions
The electrical system provides power to all the truck's electrical components. Key components include:
- Battery: Stores electrical energy and provides power to start the engine.
- Alternator: Generates electrical power to recharge the battery and power the electrical system while the engine is running.
- Starter Motor: Cranks the engine to start it.
- Wiring Harness: A network of wires that connects all the electrical components.
- Fuses and Circuit Breakers: Protect the electrical system from overloads.
- Lights: Provide visibility for driving at night and signaling other drivers.
- Sensors: Monitor various engine and vehicle parameters, providing data to the engine control unit (ECU).
- ECU (Engine Control Unit): A computer that controls various engine functions, such as fuel injection and ignition timing.
Pro Tips From Us: Regularly check your battery terminals for corrosion and clean them as needed to ensure a good electrical connection.
Specific Truck Type Parts:
Beyond the general parts, certain truck types have specialized components.
- Semi-Trucks: These often feature fifth-wheel couplings for trailer attachment, air brake systems, and specialized suspension systems designed for heavy loads. Understanding terms like "tractor," "trailer," and "kingpin" are essential.
- Dump Trucks: Key parts include the hydraulic lift system for raising the dump bed, the dump bed itself, and reinforced chassis components to handle the heavy loads.
- Box Trucks: These have enclosed cargo areas and often feature roll-up doors, lift gates, and specialized shelving or racking systems.
Navigating Parts Catalogs and Online Resources:
Knowing the names is just the first step. Learning how to find the parts you need is equally important.
- Parts Catalogs: Most manufacturers and parts suppliers offer detailed parts catalogs, either in print or online. These catalogs typically include exploded diagrams and part numbers.
- VIN (Vehicle Identification Number): The VIN is a unique identifier for your truck. Using your VIN when searching for parts will ensure you get the correct components for your specific vehicle.
- Online Parts Retailers: Numerous online retailers specialize in truck parts. Be sure to choose reputable suppliers and compare prices before making a purchase.
- OEM vs. Aftermarket Parts: OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts are made by the same company that made the original parts for your truck. Aftermarket parts are made by other companies and may be less expensive.
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics:
Understanding truck parts names can also help you troubleshoot problems.
- Listen to Your Truck: Pay attention to unusual noises, vibrations, or smells. These can often indicate a problem with a specific part.
- Check for Leaks: Leaks of oil, coolant, or other fluids can indicate a failing seal or gasket.
- Use a Code Reader: If your truck has a check engine light illuminated, use a code reader to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes can help you identify the source of the problem.
External Link: For more information on diagnostic trouble codes, check out this resource from the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
Conclusion:
Mastering truck parts names is a valuable investment for anyone involved in the trucking industry. Whether you're a truck owner, mechanic, or fleet manager, having a solid understanding of truck terminology will improve communication, reduce costs, and enhance safety. This comprehensive guide has provided a detailed overview of the major truck parts names, covering everything from the engine and drivetrain to the chassis, body, and electrical systems. By familiarizing yourself with these terms, you'll be well-equipped to navigate the complex world of truck maintenance and repair. Remember to always consult your truck's owner's manual and seek professional assistance when needed.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you'd like any revisions or further expansions on specific sections.